5.6 Compounds with More Than One Chirality Centers
5.6 具有多个手性中心的化合物
5.6.1 Diastereomers 5.6.1 非对映异构体
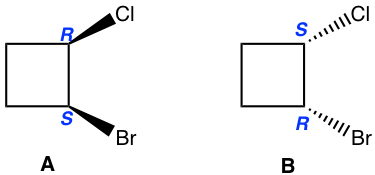
It is very common for there to be more than one chirality centers in an organic compound. For the example of 2-bromo-3-chlorobutane below, there are 2 chirality centers, C2 and C3. As each chirality center has two possible configurations, R and S, the total number of possible stereoisomers for this compound is four, with configurations on C2 and C3 as RR, SS, RS and SR, respectively.
有机化合物中存在多个手性中心是很常见的。对于下面的2-溴-3-氯丁烷的例子,有2个手性中心,C2和C3。由于每个手性中心有两种可能的构型,R和S,因此该化合物可能的立体异构体总数为四种,其中C2和C3上的构型分别为RR、SS、RS和SR。

As a general rule, for a compound that has n chirality centers, the maximum number of stereoisomers for that compound is 2n.
作为一般规则,对于具有 n 个手性中心的化合物,该化合物的立体异构体的最大数量为 2 n 。
The four stereoisomers of 2-bromo-3-chlorobutane consist of two pairs of enantiomers. Stereoisomers A and B are a pair of non-superimposable mirror images, so they are enantiomers. So are the isomers C and D. What then is the relationship between isomer A and C?
2-溴-3-氯丁烷的四种立体异构体由两对对映体组成。立体异构体A和B是一对不可重合的镜像,因此它们是对映异构体。异构体C和D也是如此。那么异构体A和C之间是什么关系呢?
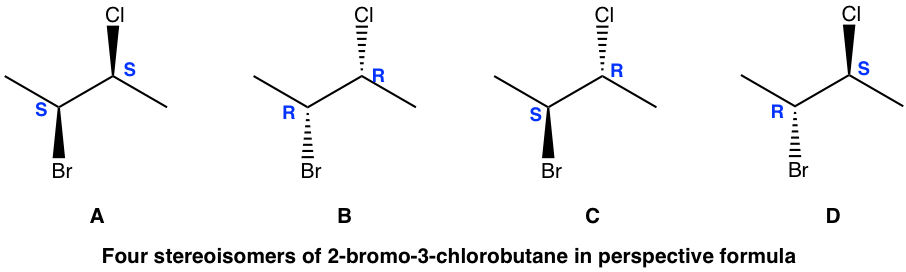
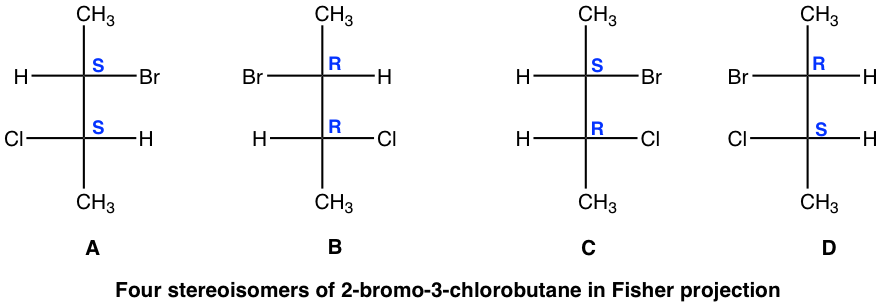
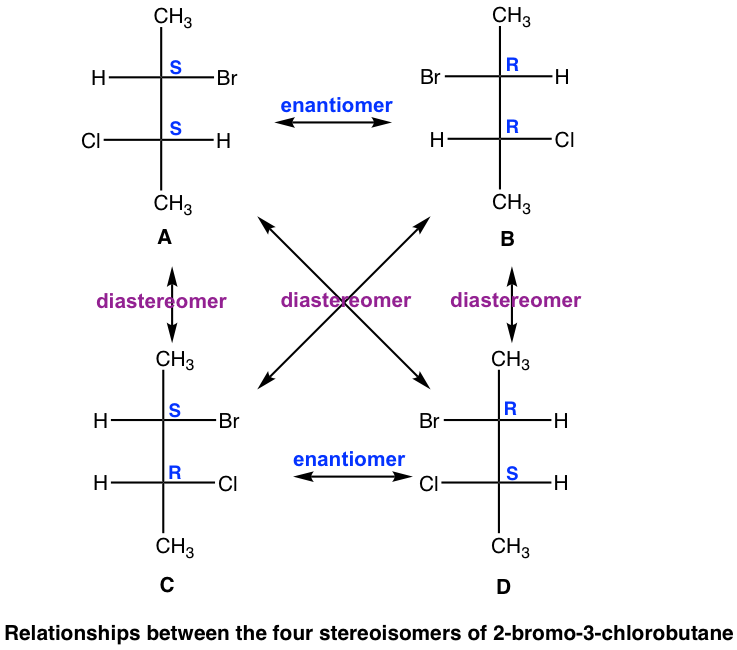
A and C are not identical, not enantiomers, and they are stereoisomers (have the same bonding but differ in the spatial arrangement of groups). This type of stereoisomer is defined as a diastereomer. Diastereomers are stereoisomers that are not enantiomers. For the four stereoisomers here, there are four pairs of diastereomers: A and C, A and D, B and C, and B and D. The relationship between the four stereoisomers can be summarized as:
A和C不相同,不是对映体,它们是立体异构体(具有相同的键合,但基团的空间排列不同)。这种类型的立体异构体被定义为非对映异构体。非对映异构体是非对映异构体的立体异构体。对于这里的四种立体异构体来说,有四对非对映异构体:A和C、A和D、B和C、B和D。四种立体异构体之间的关系可以概括为:
With the introduction of the diastereomer concept, the way to categorize isomers can be revised, and the summary in Fig. 5.1a can be replaced by the updated version in Fig. 5.6a. The stereoisomer then has two sub-types; enantiomers and diastereomers, because any stereoisomers that are not enantiomers can always be called diastereomers. Based on such a definition, the geometric isomers we learned about earlier also belong to the diastereomer category.
随着非对映异构体概念的引入,异构体的分类方式可以被修改,图5.1a中的摘要可以被图5.6a中的更新版本所取代。立体异构体有两个子类型:对映异构体和非对映异构体,因为任何不是对映异构体的立体异构体都可以称为非对映异构体。基于这样的定义,我们前面了解到的几何异构体也属于非对映异构体范畴。
图 5.6a 更新后的异构体总结
As mentioned earlier, enantiomers are very similar to each other, and they share the same physical properties except optical activity (the opposite sign for a specific rotation). Enantiomers also generally have same chemical properties, except for the reaction with other chiral reagents (not topics in this course).
如前所述,对映体彼此非常相似,并且除了旋光性(比旋光度的符号相反)之外,它们具有相同的物理性质。对映体通常也具有相同的化学性质,除了与其他手性试剂的反应(不是本课程的主题)。
However, diastereomers are not that closely related. Diastereomers have different physical properties, for example, different b.p., color, density, polarity, solubility, etc. They also have different chemical properties.
然而,非对映异构体的相关性并不那么密切。非对映异构体具有不同的物理性质,例如不同的沸点、颜色、密度、极性、溶解度等。它们还具有不同的化学性质。
Next, we will go through examples of cyclic compounds to see how the new concept of the diastereomer relates to the knowledge of cyclic compounds we learned before.
接下来,我们通过环状化合物的例子来看看非对映异构体的新概念与我们之前学过的环状化合物的知识有何联系。
Examples 例子
Draw the structures of all the stereoisomers for 1-bromo-2-chlorocyclobutane, and indicate the relationship between any two stereoisomers.
画出1-溴-2-氯环丁烷所有立体异构体的结构,并指出任意两个立体异构体之间的关系。
Approach: 方法:
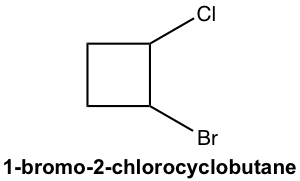
There are two chirality centers for a 1-bromo-2-chlorocyclobutane molecule. So, the maximum number of stereoisomers is four. To work on the stereoisomers for cyclic compounds, we can start with a cis/trans isomer and then check whether the enantiomer applies to each case.
1-溴-2-氯环丁烷分子有两个手性中心。因此,立体异构体的最大数量是四种。为了研究环状化合物的立体异构体,我们可以从顺式/反式异构体开始,然后检查对映异构体是否适用于每种情况。
Solution: 解决方案:
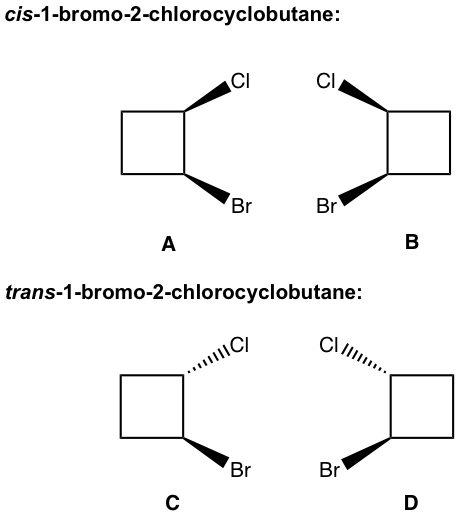
There are two cis-isomers: A and B, and they are enantiomers of each other; similarly, there are also two trans-isomers: C and D that are enantiomers of each other as well.
有两种顺式异构体:A和B,互为对映体;同样,也有两种反式异构体:C 和 D,它们也是彼此的对映体。
The relationship between any of the cis-isomers to any of the trans-isomer is diastereomers (A and C, A and D, B and C, and B and D). Since they are geometric isomers, and as we learned earlier geometric isomers can also be called diastereomers.
任何顺式异构体与任何反式异构体之间的关系都是非对映异构体(A 和 C、A 和 D、B 和 C、以及 B 和 D)。由于它们是几何异构体,并且正如我们之前了解到的,几何异构体也可以称为非对映异构体。
All geometric isomers are diastereomers (it is always correct to call a pair of geometric isomers diastereomers); however, not all diastereomers are geometric isomers!
所有几何异构体都是非对映异构体(将一对几何异构体称为非对映异构体总是正确的);然而,并非所有非对映异构体都是几何异构体!
Examples: 例子:
What is the relationship between the following pair of compounds, enantiomers, identical, diastereomers, constitutional isomers, non-isomers?
下列一对化合物、对映异构体、相同异构体、非对映异构体、结构异构体、非异构体之间有什么关系?
1.
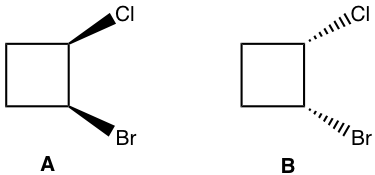
Method I: The basic way is to determine the configuration of each chirality center. As shown below that the configuration for both chirality centres are right opposite between the structure A and B. So they are enantiomers.
方法一:基本方法是确定各个手性中心的构型。如下图所示,结构A和结构B的两个手性中心的构型完全相反,因此它们是对映体。
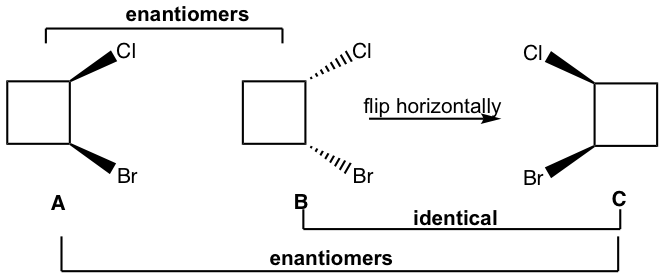
Method II: For the cyclic structures, sometimes rotate or flip a given structure in a certain way helps us to tell the relationship (using the molecular model helps the rotate or flip part). For this example, flipping structure B horizontally leads to structure C, B and C are identical. Then it is easy to tell that A and C are just non-superimposable mirror images to each other, so A and C are enantiomers, then A and B are enantiomers as well.
方法二:对于环状结构,有时以某种方式旋转或翻转给定的结构有助于我们说出其中的关系(使用分子模型有助于旋转或翻转部分)。对于此示例,水平翻转结构 B 会导致结构 C,B 和 C 是相同的。那么很容易看出A和C只是互不重叠的镜像,所以A和C是对映体,那么A和B也是对映体。
If this method looks confusing to you, then you can stick to Method I.
如果这个方法让你感到困惑,那么你可以坚持使用方法一。
2.
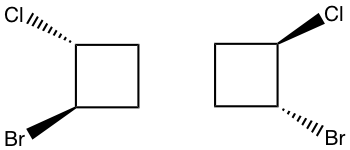
You can use either of the above methods, the answer is “identical”.
您可以使用上述任何一种方法,答案是“相同”。
5.6.2 Meso compound 5.6.2 内消旋化合物
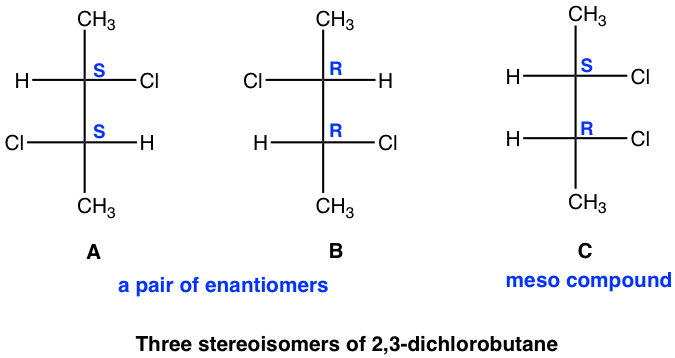
Next, we will see another example of a compound containing two chirality centers, 2,3-dichlorobutane, a compound that has the same substituents on C2 and C3 carbons.
接下来,我们将看到另一个含有两个手性中心的化合物的例子,2,3-二氯丁烷,该化合物在 C2 和 C3 碳上具有相同的取代基。

Theoretically, there are a maximum of four stereoisomers, and the structures are shown here by Fisher projections here.
理论上,最多有四种立体异构体,其结构通过费舍尔投影显示。

Stereoisomer A and B are non-superimposable mirror images, so they are enantiomers.
立体异构体A和B是不可重叠的镜像,因此它们是对映体。
We will take a detailed look at stereoisomer C and D. Yes, they are mirror images, but are they really non-superimposable? If isomer C is rotated 180° (180° rotation still gets the same structure back for a Fisher projection), then it could get superimposed on isomer D. So, isomer C and D are superimposable mirror images, which means they are the same, identical!
我们将详细研究立体异构体C和D。是的,它们是镜像,但它们真的是不可叠加的吗?如果异构体 C 旋转 180°(对于费舍尔投影,180° 旋转仍然得到相同的结构),那么它可以叠加在异构体 D 上。因此,异构体 C 和 D 是可叠加的镜像,这意味着它们是相同的,完全相同的!
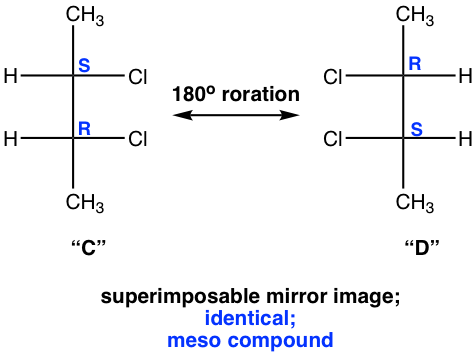
Then “C” and “D” are just different drawings for the same stereoisomer. The next question is whether this stereoisomer is chiral. We have confirmed that this isomer does get superimposed on its mirror image, which means it is achiral.
那么“C”和“D”只是同一立体异构体的不同图形。下一个问题是这种立体异构体是否是手性的。我们已经证实该异构体确实叠加在其镜像上,这意味着它是非手性的。
This is so weird! Can a compound that contains two chirality centers (C2 and C3) be achiral?
这太奇怪了!包含两个手性中心(C2 和 C3)的化合物可以是非手性的吗?
Yes, it can! A compound that is achiral but contains chirality centers is called a meso compound. A meso compound is achiral and optical inactive (it does NOT rotate the plane of polarization of plane-polarized light), but it does have multiple chirality centers.
是的,它可以!非手性但含有手性中心的化合物称为内消旋化合物。内消旋化合物是非手性且光学非活性的(它不会旋转平面偏振光的偏振面),但它确实具有多个手性中心。
Because that one stereoisomer is a meso compound, the total number of stereoisomers for 2,3-dichlorobutane is three.
由于一种立体异构体是内消旋化合物,因此2,3-二氯丁烷的立体异构体总数为三种。
Attention, 2n is the maximum number of stereoisomers. Some compounds may have less than the maximum, because of the existence of meso compounds.
注意,2 n 是立体异构体的最大数量。由于内消旋化合物的存在,某些化合物的含量可能低于最大值。
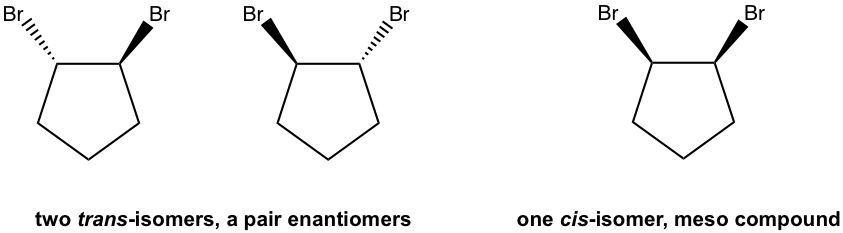
Examples: Draw all the stereoisomers of 1,2-dibromocyclopentane.
示例:画出 1,2-二溴环戊烷的所有立体异构体。
Solutions: there are total three stereoisomers.
解:共有三种立体异构体。
Exercises 5.8 练习5.8
Draw all stereoisomers for 1-ethyl-3-methylcyclohexane.
画出 1-乙基-3-甲基环己烷的所有立体异构体。Draw all stereoisomers for 1-ethyl-4-methylcyclohexane.
画出 1-乙基-4-甲基环己烷的所有立体异构体。Draw all stereoisomers for 1,2-dimethylcyclohexane.
画出 1,2-二甲基环己烷的所有立体异构体。
Answers to Chapter 5 Practice Questions
第 5 章练习题答案
5.6.3 Chiral or achiral by looking for Plane of symmetry
5.6.3 通过寻找对称面来判断手性或非手性
The existence of chirality centers does not guarantee the chirality of a molecule, for example, of the meso compound. Following the definition of chirality always involves the comparison between the original structure and its mirror image, which requires extra work. Is there any easier way to tell whether a molecule is chiral or achiral?
手性中心的存在并不能保证分子(例如内消旋化合物)的手性。遵循手性的定义总是涉及原始结构与其镜像之间的比较,这需要额外的工作。有没有更简单的方法来判断分子是手性分子还是非手性分子?
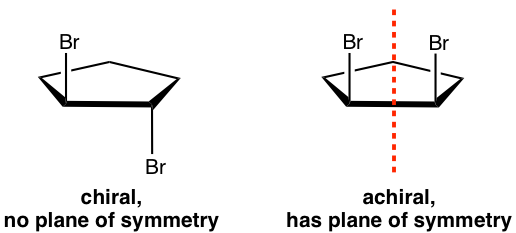
We can check the plane of symmetry. The plane of symmetry is a plane that cuts the molecule in half, and each half is the mirror image of the other.
我们可以检查对称平面。对称面是将分子切成两半的平面,每一半都是另一半的镜像。
If a molecule does have a plan of symmetry, then the molecule is achiral.
如果分子确实具有对称平面,则该分子是非手性的。A molecule that does not have a plane of symmetry in any conformation is chiral.
在任何构象中都不具有对称面的分子是手性的。
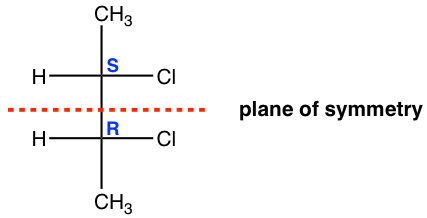
For the meso isomer of 2,3-dichlorobutane, the plane of symmetry is the plane that is labelled in the structure below.
对于 2,3-二氯丁烷的内消旋异构体,对称平面是下面结构中标记的平面。
Examples: 例子:
Determine whether the following molecule is chiral or achiral.
确定下列分子是手性分子还是非手性分子。

Solution: 解决方案:
Checking the plane of symmetry provides a quick way to determine the chirality of a molecule. But sometimes you may need to look for the proper conformation to get the plane of symmetry. See following example.
检查对称面提供了一种快速确定分子手性的方法。但有时您可能需要寻找正确的构象以获得对称平面。请参阅以下示例。
Examples: What is the relationship of the following pair of structures?
示例:以下一对结构之间的关系是什么?
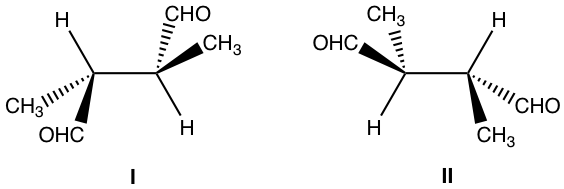
Approach: Determine the R/S configuration of each carbon.
方法:确定每个碳的 R/S 构型。
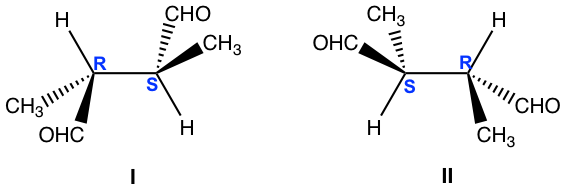
For both structures, the chirality centres are bonded with the same groups, and structure I has R and S, structure II has S and R. Are they enantiomers?
对于这两种结构,手性中心都与相同的基团键合,并且结构I具有R和S,结构II具有S和R。它们是对映体吗?
A bit further investigation is necessary to get the conclusion. Let’s rotate the groups around the 2nd chirality centre of structure I (you can use the molecular model to do the rotation, that is very helpful for visualizing the spatial arrangement of the groups):
需要进一步调查才能得出结论。让我们围绕结构 I 的 2 个 nd 手性中心旋转基团(可以使用分子模型进行旋转,这对于可视化基团的空间排列非常有帮助):

Rotation of the groups around the chirality centre does not change the configuration, however it does change the conformation to eclipsed conformation. In the eclipsed conformation, it is easier to tell that the structure has a plane of symmetry, so it is a meso compound that is achiral. Achiral compound does not have enantiomer, so structure II is also meso compound that is identical to structure I.
基团围绕手性中心的旋转不会改变构型,但它确实将构象改变为重叠构象。在重叠构象中,更容易看出该结构具有对称平面,因此它是非手性的内消旋化合物。非手性化合物没有对映体,因此结构II也是与结构I相同的内消旋化合物。
Solution: Identical 解决方案:相同
(You can rotate, or do switches to compare between the two structures, but make sure to keep track on any action. If it is easy to get lost by rotating or switch, assign R/S configuration is a safer way.)
(您可以旋转或切换来比较两种结构,但请确保跟踪任何操作。如果旋转或切换很容易迷失方向,则分配 R/S 配置是更安全的方法。)
Examples 例子
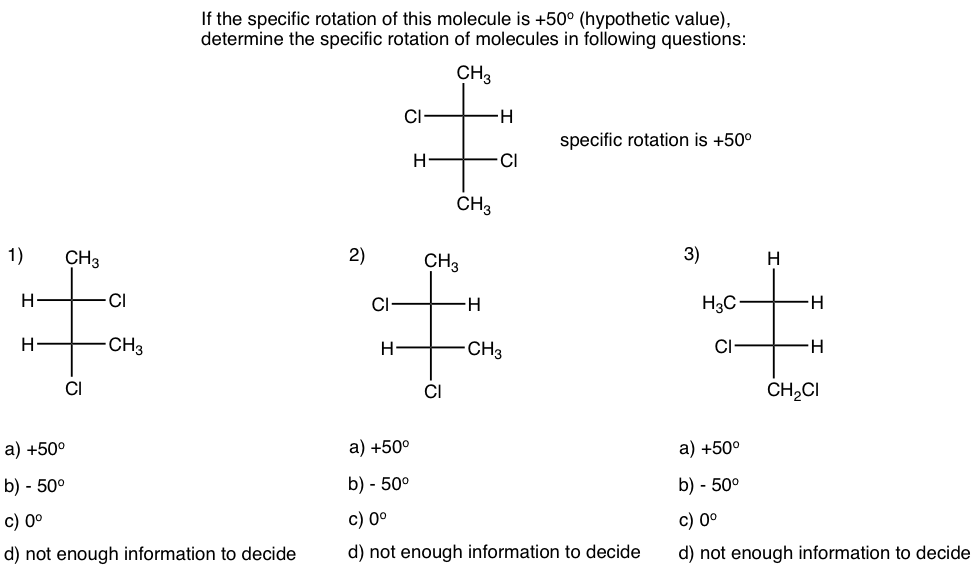
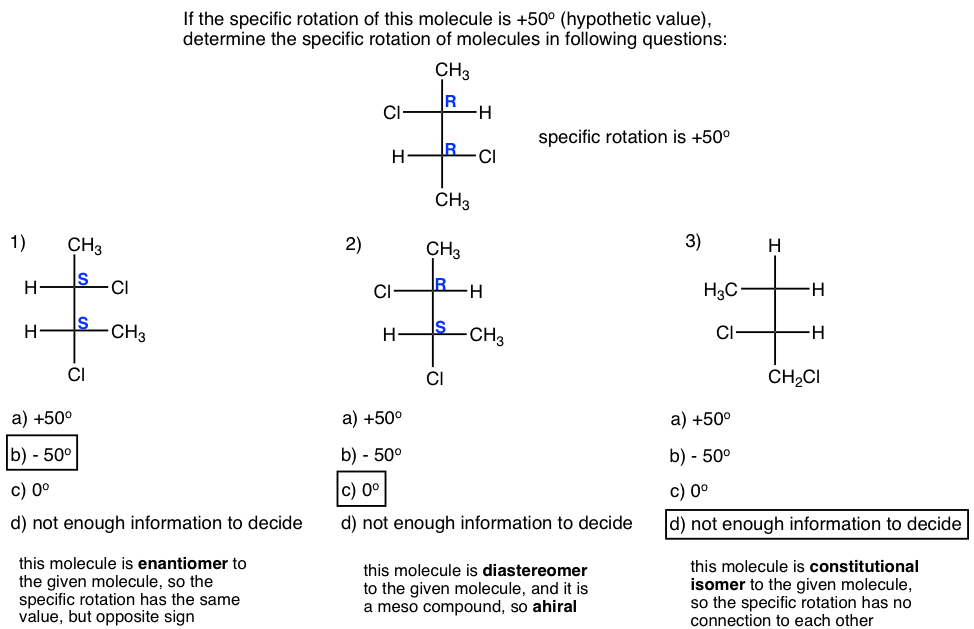
Thinking: Determine the relationship between the molecule in each question with the given one, and apply the knowledge of specific rotation.
思考:确定每一题中的分子与给定分子之间的关系,并应用比旋光知识。
Solutions: 解决方案:
来源于资源矩阵知识星球【仪器分析学苑】
更多内容看下边:
当你在仪器分析工作的时候:
是否曾为一份技术教程无处找到而发愁? 是否在遇到问题时候无人解答? 是否需要提升认知的时候google不到自己想要的答案? 是否面对日益激烈的分析行业无人分析? 是否想告别那些成天都是广告满天飞的行业社群? 这些问题在我们的知识星球都能解决,这是仪器分析行业(色谱质谱)专属的知识星球,一个属于▶仪器分析◀色谱质谱行业的优质付费社群! 商业的底层逻辑是什么,是最短时间得到最准确的信息,加入知识星球能帮你节约宝贵时间,让你专注学习,分享,交流!让你专注于学习、分享、交流和商业洽谈。通过最低的成本,你可以获得最大的价值。
经过近200个日日夜夜的积累,仪器分析学苑知识星球已经囊括了超过100+份产品技术文档,视频,经验分享,行业报告等等。
还能加入特定交流群得到本人和各位大佬的指导
及其丰富的书籍资源,也可以提供相关的技术咨询

随着资料逐渐增加,会员人数逐渐增多,每隔半年,星球价格会依据情况相应上浮,早加入,早享受,等待就是成本!
星球价格,不过一顿饭,但是星球却可以持续的给你提供价值,助力市场开拓,销售增长,职场提升。还能扩大行业链接,增加创富可能!
目前扫码就可以加入:
知识星球1:仪器分析学家的培养基地:仪器分析学苑

知识星球2:只需要某某元,一顿茶水钱,扫码有惊喜,医药投资、了解医药创业,投资,职业的平台,附带群资源

vx:加我微信咨询:关注公众号-我的-联系我们,扫码加
医药仪器创业方面的群聊:邀请制或者加入知识星球 总结不易,大佬肯赞赏否? END
声明:本公众号所有转载文章系出于传递更多信息之目的,且明确注明来源和作者,不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。所有文章仅代表作者观点,不代表本站立场。
垂直文章


