еӨ§е®¶еҘҪе‘ҖпјҢжҲ‘жҳҜжұӨеңҶгҖӮ
д»ҠеӨ©з»ҷеӨ§е®¶и®Іе…үеәҰжі•еә”з”ЁпјҢиҝҷйғЁеҲҶйўҳзӣ®жңҖеёёиҖғзҡ„е°ұжҳҜи®Ўз®—йўҳд»ҘеҸҠе®һйӘҢи®ҫи®ЎйўҳпјҢйғҪжҳҜеҲҶеҖјеҫҲй«ҳзҡ„йўҳзӣ®пјҢе»әи®®йҮҚзӮ№еӯҰд№ пјҒпјҒпјҒ
и®°еҫ—收и—Ҹе–”пҪһ

В
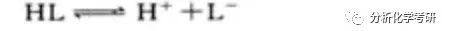
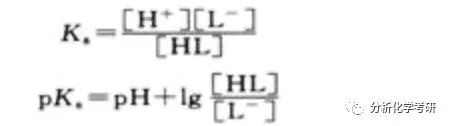
д»ҺдёҠиҝ°е…¬ејҸеҸҜзҹҘпјҢеҸӘиҰҒеңЁжҹҗдёҖзЎ®е®ҡзҡ„pHдёӢпјҢзҹҘйҒ“[HL]дёҺ[L-]зҡ„жҜ”еҖјпјҢе°ұеҸҜд»Ҙи®Ўз®—pKaгҖӮ
HLжҳҜL-дә’дёәе…ұиҪӯй…ёзўұпјҢе®ғ们зҡ„е№іиЎЎжө“еәҰд№Ӣе’ҢзӯүдәҺејұй…ёHLзҡ„еҲҶжһҗжө“еәҰcгҖӮеҸӘиҰҒдёӨиҖ…йғҪйҒөд»Һжң—дјҜ-жҜ”е°”е®ҡеҫӢпјҢе°ұеҸҜд»ҘйҖҡиҝҮжөӢе®ҡжә¶ж¶Ізҡ„еҗёе…үеәҰжұӮеҫ—[HL]е’Ң[L-]зҡ„жҜ”еҖјгҖӮ
е…·дҪ“еҒҡжі•пјҡ
й…ҚеҲ¶nдёӘжө“еәҰcзӣёзӯүиҖҢpHдёҚеҗҢзҡ„HLжә¶ж¶ІпјҢеңЁжҹҗдёҖзЎ®е®ҡзҡ„жіўй•ҝдёӢпјҢз”Ё
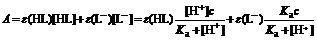 В В В В В гҖҒ
В В В В В гҖҒ
еңЁй«ҳй…ёеәҰд»ӢиҙЁдёӯпјҢеҸҜд»Ҙи®Өдёәжә¶ж¶ІдёӯиҜҘй…ёеҸӘд»ҘHLеһӢдҪ“еӯҳеңЁпјҢд»ҚеңЁд»ҘдёҠзЎ®е®ҡзҡ„жіўй•ҝдёӢжөӢе®ҡеҗёе…үеәҰпјҢеҲҷ

 В В В В В 1 В В В В В В
В В В В В 1 В В В В В В иҖҢеңЁзўұжҖ§д»ӢиҙЁдёӯпјҢеҸҜд»Ҙи®ӨдёәиҜҘй…ёдё»иҰҒд»ҘL-еһӢдҪ“еӯҳеңЁпјҢиҝҷж—¶дҫқ然еңЁд»ҘдёҠжіўй•ҝдёӢжөӢйҮҸеҗёе…үеәҰпјҢеҲҷ

 В В В В В В В 2
В В В В В В В 2е°ҶејҸ1гҖҒ2д»Је…Ҙи§ЈзҰ»еёёж•°иЎЁиҫҫејҸпјҢж•ҙзҗҶеҗҺпјҢеҫ—
 В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В
В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В жҲ–В В В В В В В В В В В В В В В
 В В В В В В В В В В
В В В В В В В В В В дёҠејҸжҳҜз”Ёе…үеәҰжі•жөӢе®ҡдёҖе…ғејұй…ёзҰ»и§Јеёёж•°зҡ„еҹәжң¬е…ізі»ејҸгҖӮ
ејҸдёӯAпјҲHLпјүгҖҒAпјҲL-пјүеҲҶеҲ«дёәејұй…ёе®ҡйҮҸең°д»ҘHLгҖҒL-еһӢдҪ“еӯҳеңЁж—¶жә¶ж¶Ізҡ„еҗёе…үеәҰпјҢиҜҘдёӨеҖјжҳҜдёҚеҸҳзҡ„пјӣAдёәжҹҗдёҖзЎ®е®ҡpHж—¶жә¶ж¶Ізҡ„еҗёе…үеәҰгҖӮ
дёҠиҝ°еҗ„еҖјеқҮеҸҜз”ұе®һйӘҢжөӢеҫ—пјҢе°ҶжөӢе®ҡзҡ„ж•°жҚ®д»Је…ҘејҸеӯҗе°ұеҸҜз®—еҮәpK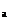 пјҢ然еҗҺеҸ–е…¶е№іеқҮеҖјпјӣд№ҹеҸҜд»Ҙе°Ҷе®һйӘҢж•°жҚ®йҮҮз”ЁзәҝжҖ§жӢҹеҗҲжі•жҲ–дҪңеӣҫжі•жұӮеҮәpKaгҖӮ
пјҢ然еҗҺеҸ–е…¶е№іеқҮеҖјпјӣд№ҹеҸҜд»Ҙе°Ҷе®һйӘҢж•°жҚ®йҮҮз”ЁзәҝжҖ§жӢҹеҗҲжі•жҲ–дҪңеӣҫжі•жұӮеҮәpKaгҖӮ
зӨәдҫӢпјҡ
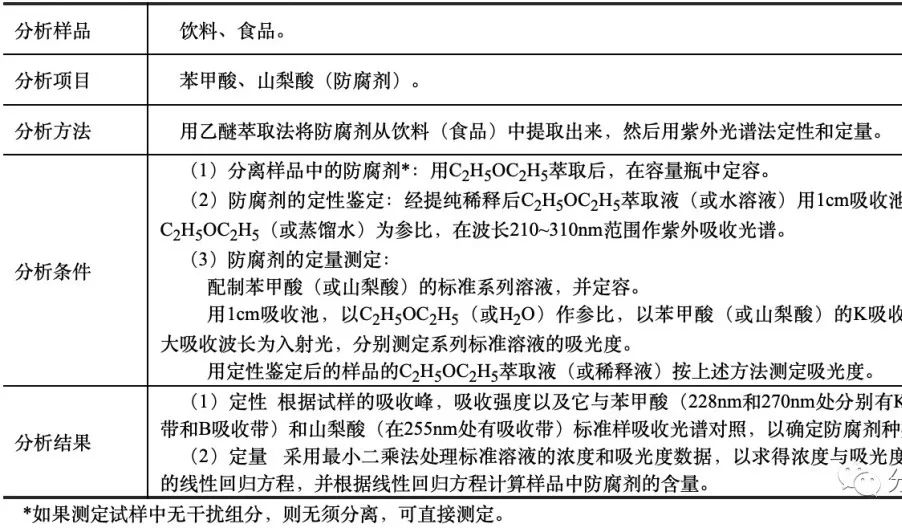
1.зҙ«еӨ–-еҸҜи§Ғеҗёж”¶е…үи°ұжі•жөӢе®ҡйҳІи…җеүӮ
В
В
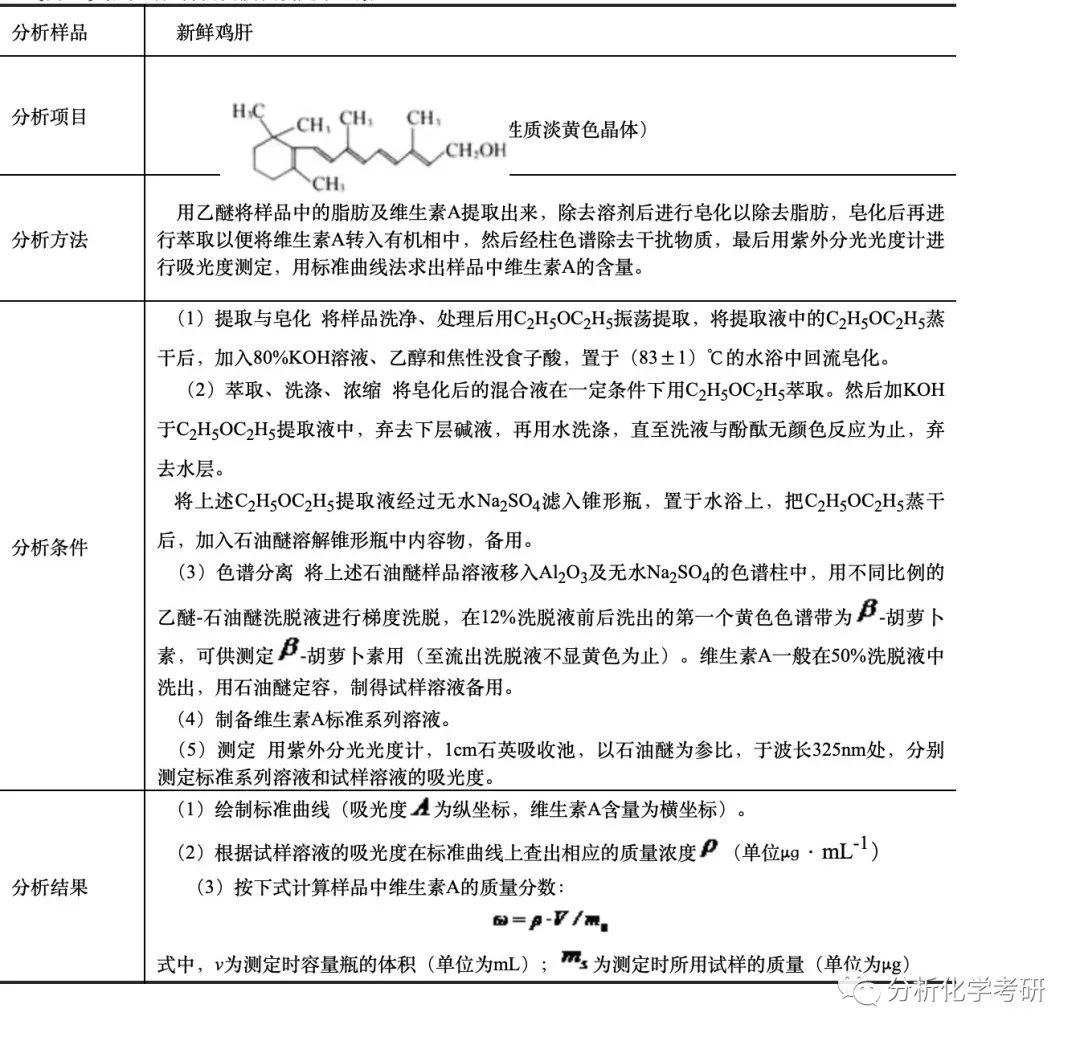
2.зҙ«еӨ–-еҸҜи§Ғе…үи°ұжөӢе®ҡз»ҙз”ҹзҙ A

- End -

В


